Contact Info
No.87, Shachong South Road, Nanming District,Guiyang city,Guizhou,China.
Cable anchor/ Pre-stressed cable anchor/ Ground anchor has many uses in civil engineering. In geotechnical applications, it is known as a ground anchor or earth anchor or mechanical anchor. It is an active in-situ soil reinforcement technique. It may be driven by the impact on the ground or in a screw fashion. In soil engineering, they are mainly used for protection against slope-stability failures, vertical excavation support, resist uplift action due to water table, etc. They can also be used for small and large applications.
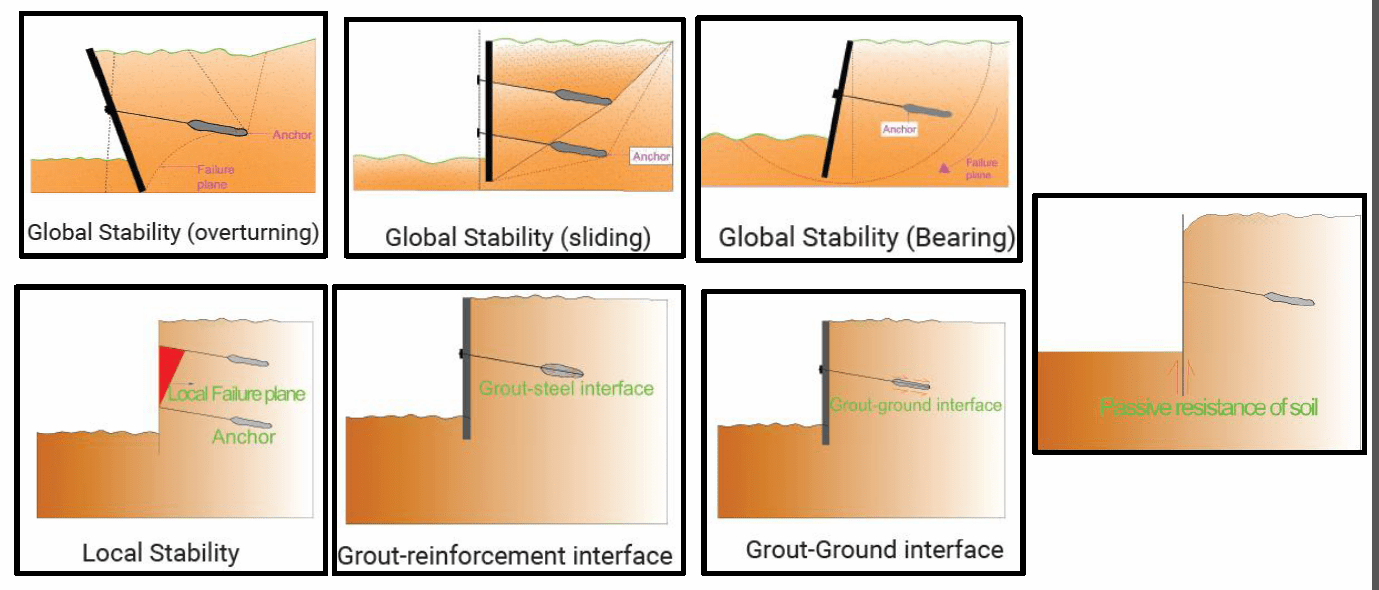
Design Consideration in Slope Stability Work
The design considerations for safety in slope stability work are the following:
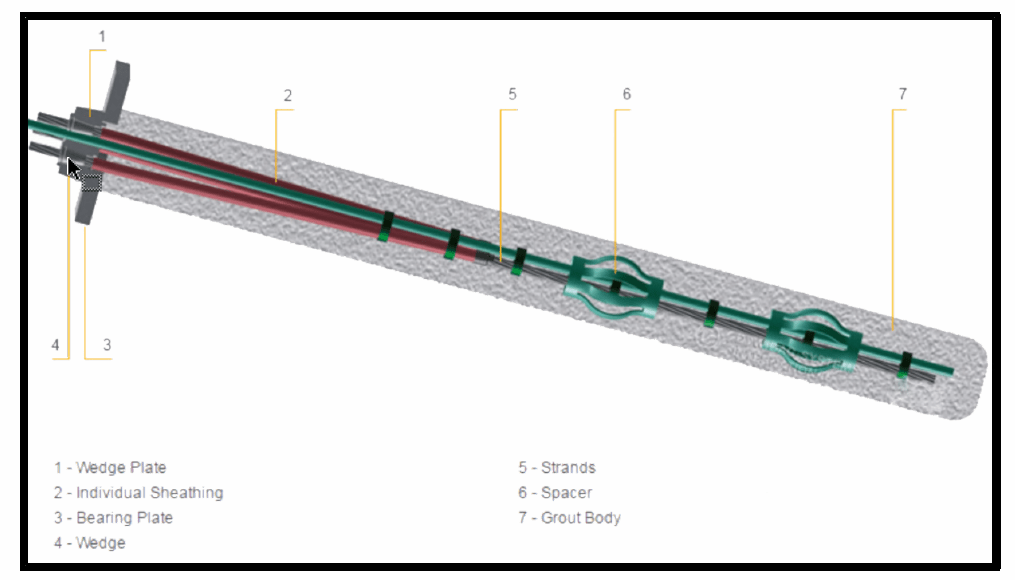
The stiffness of the wedge plate is useful in transmitting the anchor load to the bearing plate closer to the ends of the plate’s span. This prevents the bending of the bearing plate. If you have large size wedge plate, then the amount of bending of the bearing plate is reduced. Strands are useful in tying up all the cables and act as one unit. The wedge prevents the anchor part from sliding and thus keeps the ground anchor in position. Grout body is useful in maintaining a bond between the anchor and the soil.
How to Determine the Reasonable Position and Length of the Ground Anchor
This problem arises in slope reinforcement projects. One of recent method used to calculate the above is the variable-modulus elastoplastic strength reduction method or simply called as the SRM. This method is used to obtain the stress variations, strain field, factor of safety of the slope.
In this method, slope-stability done by anchor cables is modeled using surface loading. To represent the anchor reinforcement system, they are distributed in different forms of surface loading. In a study done in 2015 by Chinese researchers, it is found that, if strong anchoring is provided in the regions of high stress and large displacement, failures can be reduced. This method can also be used to identify the suitable position of the anchor cables.